High-density polyethylene (HDPE) stands out for its strong thermal, mechanical, and physical properties, making it highly versatile across various industries. A critical factor in its performance is its temperature rating, which defines its resistance to heat and plays a major role in applications like pipe systems and marine vessels. Ahmed et al.’s paper “Mechanical and Physical Properties of PP and HDPE” provides insights into HDPE’s temperature limitations and industrial strengths. We’ll go into more depth about them below:.
Thermal Properties of HDPE
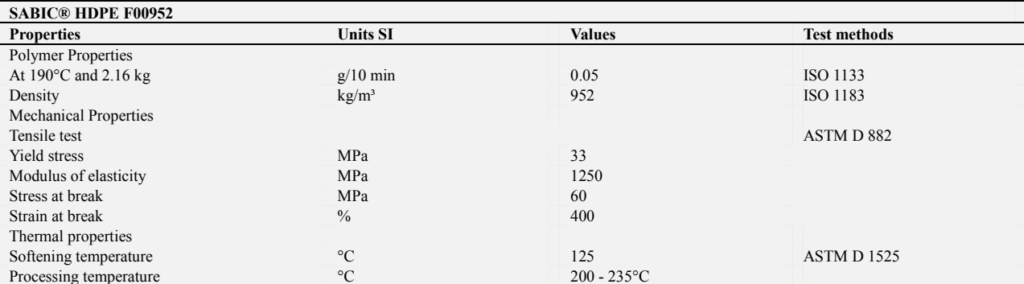
Table 1. Basic properties of HDPE (Datasheet of SABIC HDPE F00952).
SABIC’s HDPE F00952 datasheet claims the material melts at around 129°C and may be worked on between 200°C and 235°C. This enables consistent performance, even in difficult conditions. The study emphasizes HDPE’s great heat resistance, demonstrating that it begins to deteriorate around 310°C and peaks around 462°C using thermogravimetric analysis (TGA).
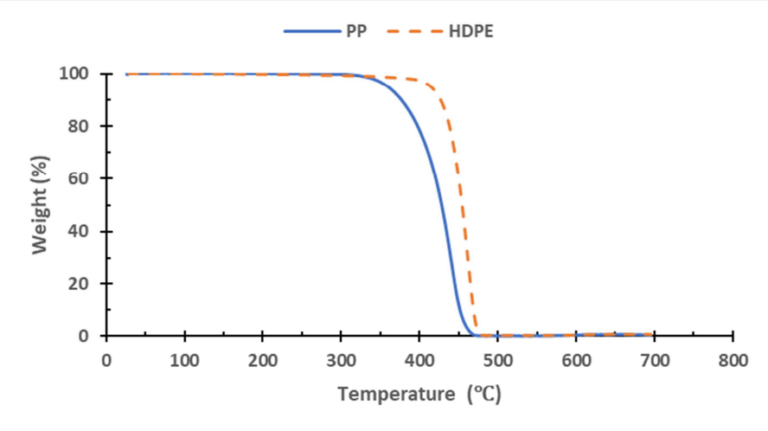
Figure 1. TG thermographs of PP and HDPE at a heating rate of 10°C/min.
In TGA tests (Figure 1), HDPE was compared with polypropylene (PP), revealing that HDPE offers superior impact resistance and flexibility. Its higher density (0.926 g/cm³) also contributes to its mechanical strength. Notably, it has minimal water absorption—just 0.045%—making it reliable in humid conditions.
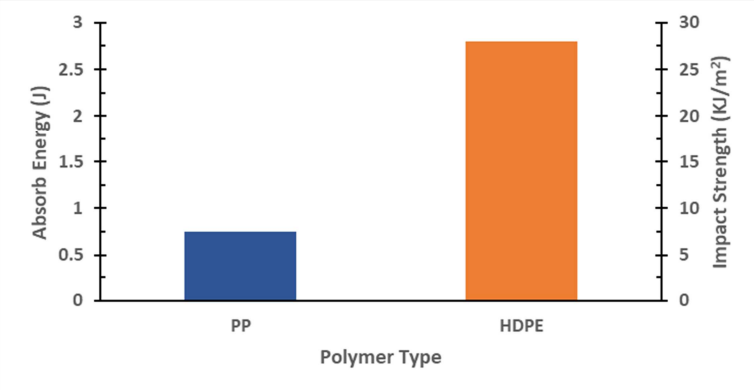
Figure 2. Absorbed energy and impact toughness of PP and HDPE.
Strength Under Pressure
DSC (Differential Scanning Calorimetry) tests revealed that HDPE has a crystallinity rate of 68%, significantly higher than PP. This gives it better stiffness and heat resistance. With a lower thermal expansion rate, HDPE also maintains its shape better at elevated temperatures—crucial for long-term structural applications.
Overall, the data confirms that HDPE offers a rare mix of thermal resilience, impact toughness, and structural flexibility, making it a go-to material for many industrial settings. Below, we explore how these properties are leveraged in real-world applications.
HDPE Applications in Vessels
Within the maritime industry, HDPE is appreciated for its resistance to corrosion and its ability to endure tough temperature and stress conditions. Recent updates to ISO 12215-5—an international standard governing vessel materials—demand that HDPE withstand harsh operational environments. It does just that, handling temperatures between -50°F (-46°C) and 180°F (82°C), making it well-suited for both icy waters and tropical climates.
Temperature limits for HDPE pipes
In the utility sector, HDPE pipes are widely used for water and gas transport thanks to their durability. These pipes are designed to operate between -40°C and 80°C (-40°F to 176°F). However, as temperatures increase toward the upper limit, the material’s strength can begin to taper.
Conclusion
HDPE is a versatile material that is known for being very strong against heat and pressure. These qualities make it appropriate for high-demand applications like pipelines and boats. To guarantee long-term performance, it becomes essential to understand the temperature restrictions and environmental interactions. Choosing the proper grade of HDPE may have a considerable impact on project efficiency and durability.
At Legacy HDPE, we specialize in crafting high-quality HDPE boats and HDPE pipes designed to perform reliably under diverse temperature and environmental conditions. For more information about our products and services, please contact us directly at Tel: 307-391-0731







